Home |
Definition & Examples of AI in the Philippines
May 15, 2025


Artificial intelligence has significantly transformed the way we live today. From streamlining autonomous, professional tasks to assisting us in our daily activities, AI has become deeply integrated into various industries. It powers almost everything, from virtual assistants and algorithms to predictive maintenance and smart city systems. This widespread adoption allows us to focus on more important or strategic work, while AI handles repetitive, time-consuming, and even complex processes. Its growing presence continues to reshape how we work, communicate, and interact with technology daily.
In this article, we’ll explore AI today, focusing on its practical applications, key benefits, and examples from Philippine companies to drive innovation and gain a competitive edge.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Photo by Nahrizul Kadri on Unsplash
Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term that describes computer systems or computer-controlled robots capable of performing tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, identifying patterns, and making decisions, ranging from simple choices to complex problem-solving, some including mathematical theorems and medical diagnoses. It relies on historical data to function and incorporates a variety of technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and robotics. AI is designed to mimic certain human characteristics, like the ability to reason, generalize, and learn from past experiences.
While some programs have reached performance levels comparable to those of human professionals and experts, there is still no AI system that flawlessly matches an individual with much everyday knowledge. Despite its widespread use, AI remains limited. It can struggle with certain nuances and adaptability, which humans can often navigate with ease.
Artificial Intelligence Today
The advancement and deployment of artificial intelligence, including generative AI and large language models (LLMs), have accelerated rapidly since ChatGPT’s rise in late 2022. This surge was driven by a scalable paradigm that leverages increasing amounts of data, computational power, energy, and investment into this growing sector. Today, nearly 65% of businesses utilize AI for cognitive tasks and even assist top coders. For example, startups like those backed by Y Combinator use AI tools that write 40%-90% of their code. AI is now surpassing human performance in a couple of tasks, such as image classification, visual reasoning, and comprehension of the English language. However, humans still outperform AI in some areas like visual common-sense reasoning, planning, and theory of mind—the ability to understand the thoughts, beliefs, and emotions of others.
With the release of leading AI technologies, training costs have risen significantly. Models such as OpenAI’s GPT-4 have estimated training costs of $78 million, while Google’s Gemini Ultra costs around $191 million, with the United States leading the global industry in owning the majority of notable models in 2023. This attracted substantial investor interest, with the generative AI sector securing $25.2 billion in investment as of 2024.
However, while AI has been shown to efficiently complete tasks more quickly, not all AI tools have undergone standardized benchmark testing, which measures an AI model’s performance. The lack of consistency in responsible AI testing shows how effectiveness can vary greatly depending on the approach and application. Moreover, public perception of AI remains mixed while many welcome the modernization and efficiency it brings to industries, there is a growing concern about AI potentially replacing jobs, threatening livelihoods, and widening social inequalities.
Ultimately, the impact of AI comes down to responsible and moderate use, where AI supports businesses and individuals rather than replacing them. This way, AI continues to serve as a powerful tool for societal advancement rather than a disruptive force that causes more harm than good.
Key Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Businesses
AI brings several benefits that can strengthen business operations. Here are the key benefits of incorporating artificial intelligence into businesses of any size:
1. Increased Operational Efficiency


Photo by Annie Spratt on Unsplash
Companies are continually seeking the best ways to enhance efficiency. By embracing the latest technologies available in the market, they can reduce redundancies and foster a culture that encourages creative problem-solving. This dual focus not only drives significant productivity gains but also positions companies to adapt to ever-changing demands and seize new opportunities.
One example is Globe using an AI-driven chatbot named “Thea”, which allows the company to respond to inquiries and concerns much faster, providing solutions for many possible instances.
2. Saves on Costs


Photo by Jakub Żerdzicki on Unsplash
Automation has emerged as a transformative force in industries, enabling businesses to reduce operational costs. By automating tasks, this allows employees to focus on higher-value work or tasks that require strategic decision-making, ultimately driving growth and profitability.
San Miguel Corporation has implemented automated systems in its manufacturing plants to streamline production processes. Additionally, SMC has equipped all its toll plazas with an ALPR camera and an RFID scanner since last year, enabling faster and barrier-free license plate recognition for all cars traveling on its expressway network.
3. Upgraded User Experience


Photo by Ant Rozetsky on Unsplash
An excellent user experience has become a more vital differentiator than ever. By prioritizing customer feedback and leveraging data analytics for future enhancements, businesses can create improved interfaces and more personalized interactions tailored to their target audience, encouraging repeat transactions and building long-term brand loyalty.
Shopee continuously improves its customers’ e-commerce experience through data analytics and customer feedback. It offers unique product recommendations and promotions, as well as user-friendly features such as one-click reordering, easy payment options, and an intuitive interface based on consumer insights.
4. Output Quality Assurance


Photo by Towfiqu barbhuiya on Unsplash
Maintaining high standards of quality is essential for every business. By leveraging AI, companies can reduce real-time errors caused by fatigue and oversight and build a strong reputation in their respective markets, ultimately leading to increased customer trust and retention. In this case, AI is heavily used in manufacturing processes of any goods, especially in larger brands such as Coca-Cola Beverages Philippines, Inc..
Artificial Intelligence in the Philippines
There are various ways in which AI is used in the Philippines. Below are 5 examples of sectors where it currently exists:
1. Banking & Finance


Photo by Eduardo Soares on Unsplash
Institutions like the Bank of the Philippine Islands (BPI) use AI tools, such as the “Track and Plan” feature on the new BPI app. This allows users to track and analyze their financial activities on the platform, providing personalized financial insights and recommendations to support them in their journey. UnionBank of the Philippines also implemented an AI-powered chatbot called “Rafa”, which assists customers with balance inquiries, loan applications, and locating branches without the need for human tellers.
2. Manufacturing


Photo by Homa Appliances on Unsplash
In the manufacturing industry, AI is widely used for smart quality control, improving accuracy in production processes. For instance, the Department of Science and Technology’s Advanced Manufacturing Center (AMCen) utilizes AI to automatically inspect and identify defective items on production lines, detecting flaws more consistently and faster than human inspectors. AI systems can also predict potential equipment failures, optimize production schedules, and ensure the best quality of products.
3. Healthcare


Photo by National Cancer Institute on Unsplash
AI has supported the healthcare industry in applications like early disease detection. St. Luke’s Medical Center uses AI-powered imaging technologies to assist radiologists, delivering faster, highly accurate analyses that enable doctors to provide precise diagnoses and treatment plans. Another example is KonsultaMD, a telemedicine platform that incorporates AI for symptom checking and preliminary patient triage.
4. Agriculture


Photo by no one cares on Unsplash
Utilizing AI is making a significant impact on Philippine agriculture. The Department of Agriculture uses AI-based platforms such as Cropital and Farmwatch, in partnership with tech companies, to assist farmers. These systems help predict weather conditions, monitor crop health through satellite imaging, and suggest best practices to maximize yield. Instead of relying solely on traditional methods, farmers can now make smarter decisions, minimizing losses in a country heavily dependent on agriculture.
5. Information Technology (IT)
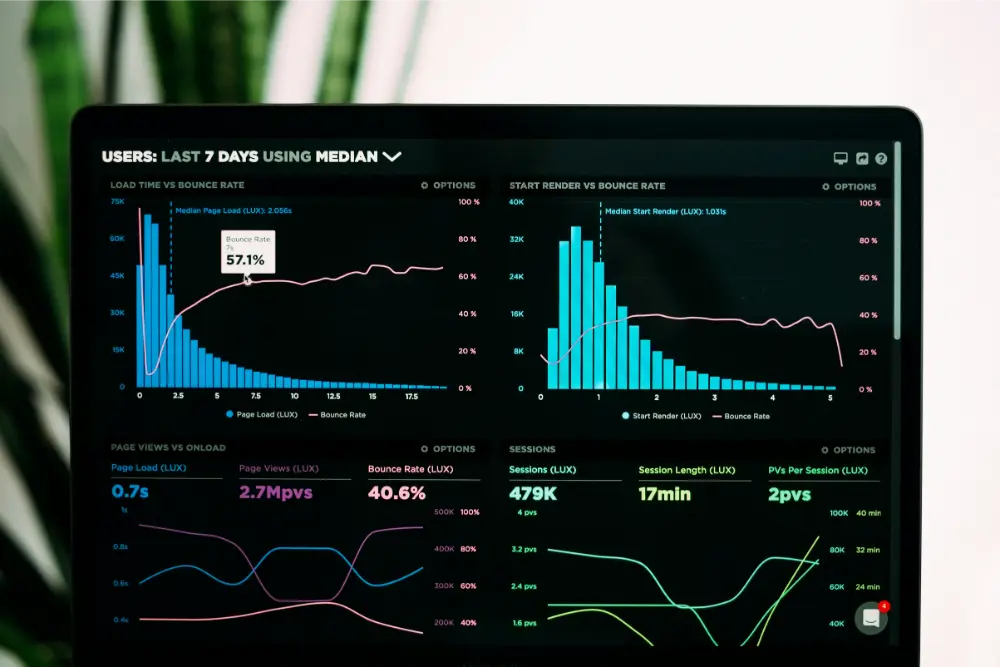

Photo by Luke Chesser on Unsplash
This sector is also predicted for AI to become a strategic trend. AI can provide predictive analytics based on given data, helping businesses make sound decisions. Sprout Solutions applies this capability to workforce management. Their platform can forecast employee turnover, absenteeism, and productivity levels, enabling companies to proactively address HR issues before they escalate. With that, businesses can optimize human resources planning, reduce operational risks, and improve overall performance.
Over time, AI has moved beyond theory, shaping today’s businesses, industries, and daily lives. Its true potential lies not just in its impressive range of capabilities, but in how responsibly we utilize it to solve problems without losing sight of our values. As AI continues to evolve, those who embrace innovation will lead the way in building a smarter, more inclusive future.
