Home |
EPON VS GPON: What’s The Difference?
October 23, 2024

In fiber-optic communication, two key technologies help transmit data across networks: Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) and Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON). Both are used to provide Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) services, which deliver internet directly to users through fiber optic cables. As the need for faster and more reliable internet grows, understanding the differences between GPON and EPON becomes important. Let’s explore these differences to help you choose the best option for your network needs.
Introduction to EPON and GPON
What is EPON?
EPON, which stands for Ethernet Passive Optical Network, utilizes Ethernet packets for data transmission, making it ideal for Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) or Fiber-to-the-Premises (FTTP) configurations. This technology provides symmetrical data rates of up to 1 Gbps in both upstream and downstream directions, ensuring efficient broadband services that include internet, voice, and video transmission.
What is GPON?
GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, uses the GPON Encapsulation Mode (GEM) to carry voice, video, and data services, including VoIP for voice. It is widely deployed in FTTH and FTTP setups and supports data rates of up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream.
Importance of Understanding the Difference
Understanding the differences between EPON and GPON is crucial for you as a consumer, business, or service provider. This knowledge significantly impacts your choice of technology for broadband deployment. GPON offers superior bandwidth and supports higher data transfer speeds, making it ideal for large-scale applications such as video streaming, cloud services, and enterprise networks that require fast, symmetrical connections. On the other hand, EPON is designed to integrate seamlessly with your existing Ethernet networks, which makes it easier and more cost-effective to deploy, especially in smaller-scale environments. By recognizing these differences, you can make informed decisions that optimize your network infrastructure, ensuring better performance, cost efficiency, and an improved user experience.
Technical Overview of GPON Technology
Key Features of GPON
GPON technology stands out due to its robust capabilities and flexibility in delivering high-speed broadband services. It supports a variety of data rates, offering both symmetrical and asymmetrical bandwidth options, which is critical for accommodating diverse user needs. With the ability to transmit up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream, GPON is particularly well-suited for high-demand applications such as streaming video, online gaming, and cloud services.
Advantages of GPON Technology
GPON technology offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive option for service providers and end-users alike. One of the most significant benefits is its higher bandwidth capabilities when compared to earlier PON standards, allowing for the simultaneous delivery of multiple services. This is particularly important in today’s data-driven world, where users expect seamless access to various applications. Furthermore, the passive architecture of GPON significantly reduces maintenance costs and energy consumption, as it does not require powered components in the distribution network. This efficiency makes GPON an appealing choice for a wide range of applications, from residential broadband to enterprise solutions, helping service providers maximize their infrastructure investments while offering reliable, high-speed connectivity to their customers.
Technical Overview of EPON Technology
Key Features of EPON
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) utilizes Ethernet packets for data transmission, enabling seamless integration with existing Ethernet networks. It supports symmetrical data rates of up to 1 Gbps and allows point-to-multipoint configurations, making bandwidth allocation efficient through the use of Ethernet frames. This architecture simplifies network management and enhances scalability, making it a popular choice for service providers optimizing their infrastructure.
Advantages of EPON Technology
EPON technology boasts several compelling advantages, especially regarding its compatibility with Ethernet, which streamlines the integration process with current network infrastructures. This compatibility translates to cost-effectiveness for service providers, as EPON does not necessitate complex equipment and can utilize standard Ethernet protocols for network management. Furthermore, the symmetrical data rates offered by EPON are particularly beneficial for applications requiring balanced upload and download speeds, catering to the needs of both residential and business customers. As such, EPON is increasingly being recognized as a viable solution in the competitive landscape of broadband technologies.
Difference Between EPON and GPON
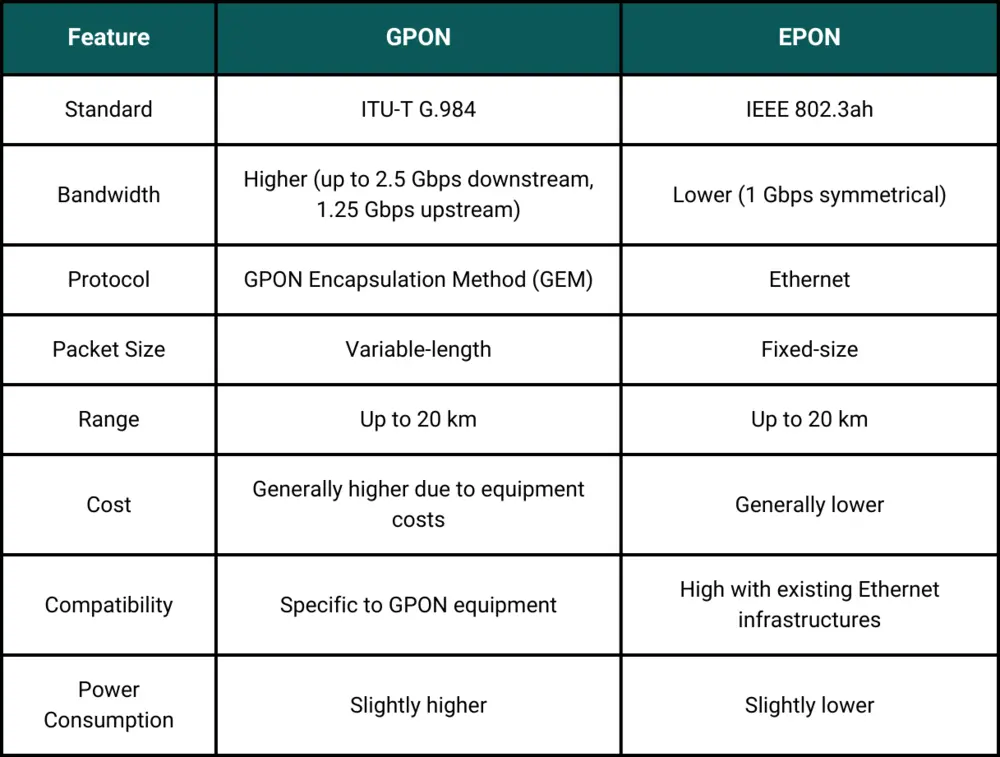

Main Differences in Technology
The primary distinction between EPON and GPON lies in their respective data transmission methods. EPON employs Ethernet packets, allowing it to seamlessly integrate with existing Ethernet networks, while GPON utilizes a hybrid approach involving ATM for voice services and Ethernet for data transmission. This fundamental difference impacts overall performance; GPON generally provides higher bandwidth capabilities of up to 2.5 Gbps, in contrast to EPON’s maximum of 1 Gbps. Additionally, GPON’s architecture is designed to efficiently support a multitude of services, whereas EPON’s Ethernet-centric system simplifies integration and network management, catering to different deployment strategies.
Performance Comparison: GPON vs EPON
When comparing performance, GPON significantly outstrips EPON in terms of bandwidth capacity, delivering up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream, whereas EPON maintains a maximum of 1 Gbps in both directions. The hybrid nature of GPON’s architecture allows for more efficient bandwidth allocation and service delivery to multiple users, making it an ideal choice for data-intensive applications. Nevertheless, EPON’s reliance on Ethernet technology offers unique advantages in terms of ease of integration and lower deployment costs. This makes EPON a viable option for specific applications where extremely high bandwidth is not a critical requirement, thus providing flexibility in network design and service offerings.
Conclusion
Both GPON and EPON have their unique strengths and weaknesses. GPON offers you higher speeds, advanced security, and enhanced performance capabilities, making it ideal for applications that require the best possible bandwidth and data management features. On the other hand, EPON is a strong contender for you if you’re budget-conscious or if you have existing Ethernet networks, as it boasts cost-effectiveness and compatibility with Ethernet.
Ultimately, your decision between GPON and EPON should be based on your specific needs and constraints. A thorough assessment considering your current and future bandwidth requirements, security concerns, budget limitations, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure will help you determine the best choice for your fiber-optic network deployment.
Recommendations for Implementation
For successful implementation, you should undertake comprehensive assessments of your target markets and infrastructure capabilities before opting for GPON or EPON. Key considerations include customer density, anticipated bandwidth requirements, and budget constraints, as these factors will greatly influence your decision-making process. Additionally, contemplating future scalability and potential upgrades ensures that the technology you choose will remain relevant as user demands evolve. By strategically planning your deployments, you can maximize efficiency and ensure long-term success in a competitive landscape.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to CloudConsole today to discuss how we can support your network deployment and help you achieve the best results for your organization.
EPON vs. GPON FAQ
1. Which offers higher speeds: EPON or GPON?
- GPON: Typically offers higher downstream speeds up to 2.5 Gbps and upstream speeds up to 1.25 Gbps.
- EPON: Offers symmetrical speeds, usually up to 1 Gbps for both downstream and upstream.
2. Are there cost differences between EPON and GPON?
- EPON: Generally less expensive, as it uses standard Ethernet technologies and simpler hardware, making it attractive for budget-conscious networks.
- GPON: More expensive due to the need for specialized GPON-compatible equipment and higher data handling capabilities.
3. Which technology is more popular in residential networks?
- GPON: Commonly used for fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) installations due to its ability to handle high-speed internet, voice, and video services efficiently in a single network.
- EPON: Although less common in residential FTTH, it’s still used in settings where Ethernet-based infrastructure is prioritized, often in enterprise and industrial applications.
4. Can EPON be upgraded to GPON?
Switching from EPON to GPON typically requires significant hardware upgrades, including replacing OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and ONT equipment, which can be costly.
5. Which is better for business use?
- GPON: Best for businesses needing stable, high-speed connections and robust QoS features, especially for mixed data types (voice, video, and data).
- EPON: More budget-friendly for businesses with standard internet requirements and where Ethernet compatibility is a priority.
